lv dilatation|dilated Lv means : 2024-10-07 Left ventricular hypertrophy changes the structure of the heart and how the heart works. The thickened left ventricle becomes weak and stiff. This prevents the lower left heart chamber from filling properly with . Description : «Chronomat» Ref. B13048 - Montre chronographe avec boîtier en acier. Cadran bleu, trois sous-compteurs dorés, date à 3h. Lunette externe graduée (manque deux cavaliers). Mouvement automatique .
0 · severe left ventricular dilation
1 · non dilated left ventricular cardiology
2 · non dilated left ventricle meaning
3 · left ventricle mildly dilated mean
4 · dilated cardiomyopathy signs and symptoms
5 · dilated cardiomyopathy echo images
6 · dilated Lv means
7 · Lv dilatation definition
Strap Change - Watch Straps Online - Breitling
lv dilatation*******Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) is a heart condition in which the left ventricle weakens, stretches, and becomes larger, making it .lv dilatation dilated Lv means left ventricular dilatation: left heart border is displaced leftward, inferiorly and posteriorly. left ventricular hypertrophy: may show rounding of the cardiac apex. Hoffman . Reduced left ventricular (LV) ejection fraction increases the risk of ventricular arrhythmias; however, LV ejection fraction has a low sensitivity to predict .
Left ventricular hypertrophy changes the structure of the heart and how the heart works. The thickened left ventricle becomes weak and stiff. This prevents the lower left heart chamber from filling properly with . Dilated cardiomyopathy causes your heart’s main pumping chamber to expand. This decreases its ability to pump blood out to your body, putting you at risk for .
Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) is a myocardial disease characterised by ventricular dilatation and global myocardial dysfunction (ejection fraction < 40%). Patients usually present with symptoms of .
lv dilatation Left ventricular dilatation is a well-recognized precursor of ventricular dysfunction and congestive heart failure after myocardial infarction. The effect of left .
dilated Lv means Left ventricular dilatation is a well-recognized precursor of ventricular dysfunction and congestive heart failure after myocardial infarction. The effect of left .Dilated cardiomyopathy is when a heart's main pumping chamber (left ventricle) is enlarged. Learn symptoms and treatments of this genetic heart condition.
Left ventricular (LV) diameter is routinely measured on the echocardiogram but has not been jointly evaluated with the ejection fraction (EF) for risk stratification of .
Symptoms of dilated cardiomyopathy — such as fatigue and shortness of breath — can mimic other health conditions. A person with dilated cardiomyopathy might not notice any symptoms at first. But dilated cardiomyopathy can become life-threatening. It's a common cause of heart failure. Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) is a heart condition in which the left ventricle weakens, stretches, and becomes larger, making it harder for the heart to pump effectively. left ventricular dilatation: left heart border is displaced leftward, inferiorly and posteriorly. left ventricular hypertrophy: may show rounding of the cardiac apex. Hoffman-Rigler sign. Shmoo sign. Echocardiography. Reduced left ventricular (LV) ejection fraction increases the risk of ventricular arrhythmias; however, LV ejection fraction has a low sensitivity to predict ventricular arrhythmias. LV dilatation and mass may be useful to further risk‐stratify for ventricular arrhythmias.
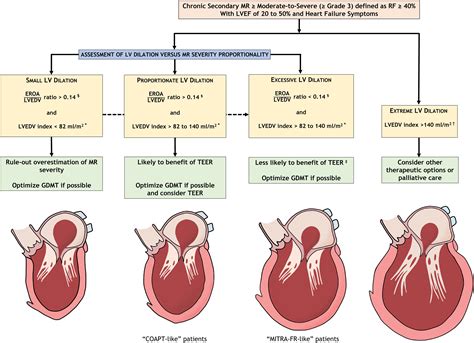
Left ventricular hypertrophy changes the structure of the heart and how the heart works. The thickened left ventricle becomes weak and stiff. This prevents the lower left heart chamber from filling properly with blood. As a .
Dilated cardiomyopathy causes your heart’s main pumping chamber to expand. This decreases its ability to pump blood out to your body, putting you at risk for heart failure. The condition affects each person differently. Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) is a myocardial disease characterised by ventricular dilatation and global myocardial dysfunction (ejection fraction < 40%). Patients usually present with symptoms of biventricular failure, e.g. . Left ventricular dilatation is a well-recognized precursor of ventricular dysfunction and congestive heart failure after myocardial infarction. The effect of left ventricular dilatation on.Dilated cardiomyopathy is when a heart's main pumping chamber (left ventricle) is enlarged. Learn symptoms and treatments of this genetic heart condition.
Left ventricular (LV) diameter is routinely measured on the echocardiogram but has not been jointly evaluated with the ejection fraction (EF) for risk stratification of sudden cardiac death (SCD). Methods and Results.

Symptoms of dilated cardiomyopathy — such as fatigue and shortness of breath — can mimic other health conditions. A person with dilated cardiomyopathy might not notice any symptoms at first. But dilated cardiomyopathy can become life-threatening. It's a common cause of heart failure. Symptoms of dilated cardiomyopathy — such as fatigue and shortness of breath — can mimic other health conditions. A person with dilated cardiomyopathy might not notice any symptoms at first. But dilated cardiomyopathy can become life-threatening. It's a common cause of heart failure.
Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) is a heart condition in which the left ventricle weakens, stretches, and becomes larger, making it harder for the heart to pump effectively.
left ventricular dilatation: left heart border is displaced leftward, inferiorly and posteriorly. left ventricular hypertrophy: may show rounding of the cardiac apex. Hoffman-Rigler sign. Shmoo sign. Echocardiography. Reduced left ventricular (LV) ejection fraction increases the risk of ventricular arrhythmias; however, LV ejection fraction has a low sensitivity to predict ventricular arrhythmias. LV dilatation and mass may be useful to further risk‐stratify for ventricular arrhythmias.
Left ventricular hypertrophy changes the structure of the heart and how the heart works. The thickened left ventricle becomes weak and stiff. This prevents the lower left heart chamber from filling properly with blood. As a .
Dilated cardiomyopathy causes your heart’s main pumping chamber to expand. This decreases its ability to pump blood out to your body, putting you at risk for heart failure. The condition affects each person differently. Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) is a myocardial disease characterised by ventricular dilatation and global myocardial dysfunction (ejection fraction < 40%). Patients usually present with symptoms of biventricular failure, e.g. . Left ventricular dilatation is a well-recognized precursor of ventricular dysfunction and congestive heart failure after myocardial infarction. The effect of left ventricular dilatation on.
Breitling Navitimer 1884 Limited Edition. In addition to a slide rule and chronograph, the Breitling Navitimer 1884 features a calendar function and 24-hour display, making it one of the .
lv dilatation|dilated Lv means






